GALAXY

A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter.
Galaxies have been categorized according to their apparent shape (usually referred to as their visual morphology). A common form is the elliptical galaxy, which has an ellipse-shaped light profile.
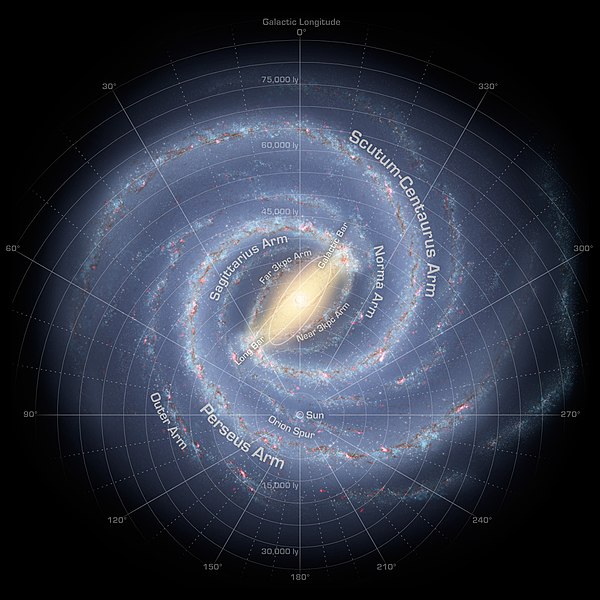
MILKY WAY GALAXY
MILKY WAY GALAXY MAP
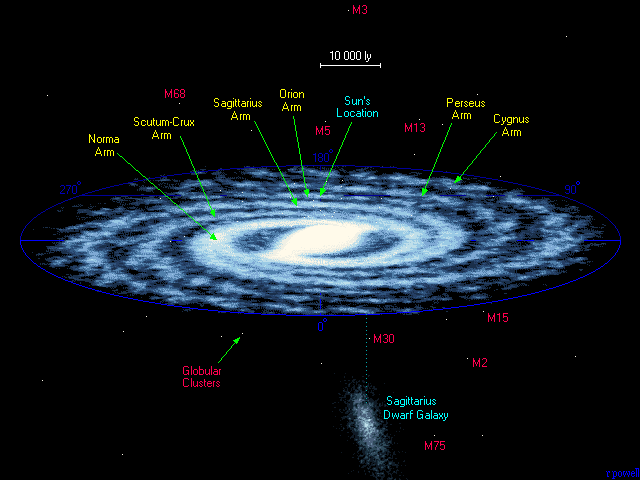
This map shows the full extent of the Milky Way galaxy - a spiral galaxy of at least two hundred billion stars. Our Sun is buried deep within the Orion Arm about 26 000 light years from the centre. Towards the centre of the Galaxy the stars are packed together much closer than they are where we live. Notice also the presence of small globular clusters of stars which lie well outside the plane of the Galaxy, and notice too the presence of a nearby dwarf galaxy - the Sagittarius dwarf - which is slowly being swallowed up by our own galaxy.
THE ORION ARM
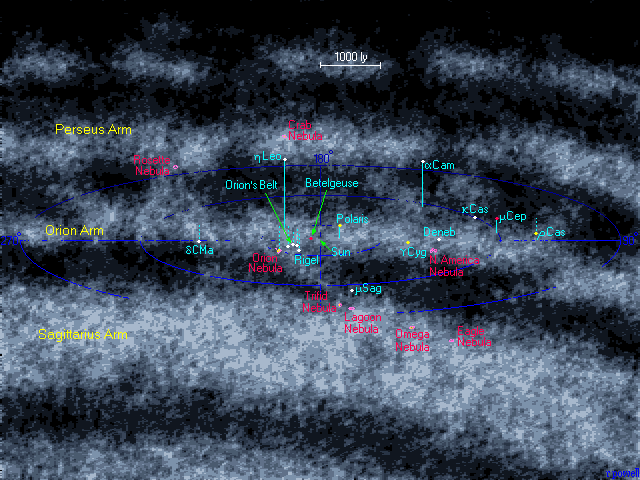
This is a map of our corner of the Milky Way galaxy. The Sun is located in the Orion Arm - a fairly minor arm compared with the Sagittarius Arm, which is located closer to the galactic centre. The map shows several stars visible with the naked eye which are located deep within the Orion arm. The most notable group of stars here are main stars in the constellation of Orion - from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant stars, thousands of times more luminous than the Sun. The most luminous star on the map is Rho Cassiopeia (ρ Cas) - to us 4000 light years away, it is a dim naked eye star, but in reality it is a huge supergiant star 100 000 times more luminous than our Sun.
THE SOLAR NEIGHBORHOOD
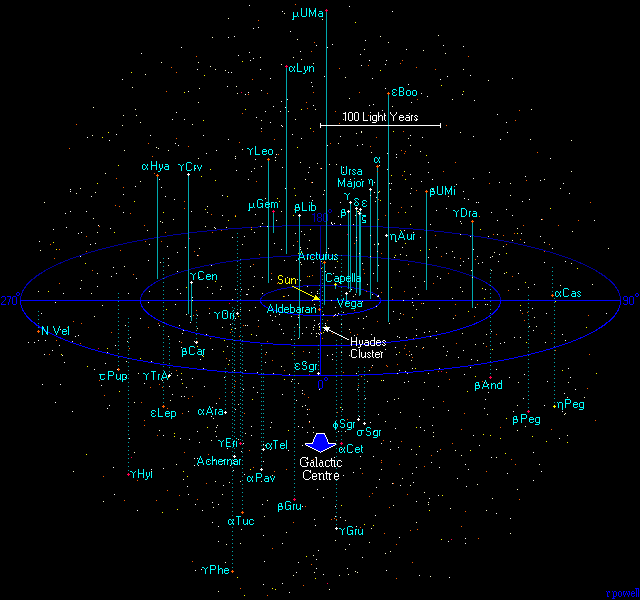
This map is a plot of the 1500 most luminous stars within 250 light years. All of these stars are much more luminous than the Sun and most of them can be seen with the naked eye. About one third of the stars visible with the naked eye lie within 250 light years, even though this is only a tiny part of our galaxy.
STAR WITHIN 50 LIGHT YEARS
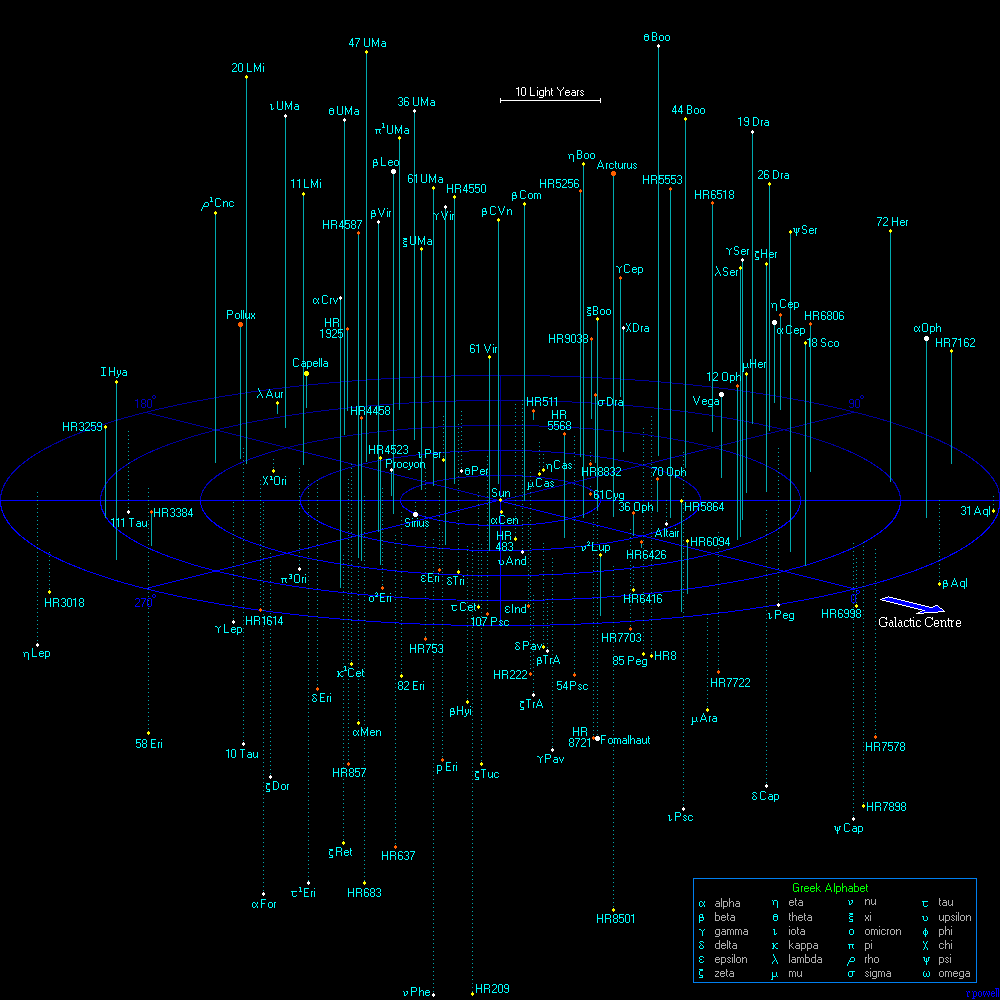
This is a map of every star within 50 light years visible with the naked eye from Earth. There are 133 stars marked on this map. Most of these stars are very similar to the Sun and it is probable that there are many Earth-like planets around these stars. There are roughly 1400 star systems within this volume of space containing 2000 stars, so this map only shows the brightest 10% of all the star systems, but most of the fainter stars are red dwarfs.
THE NEAREST STARS
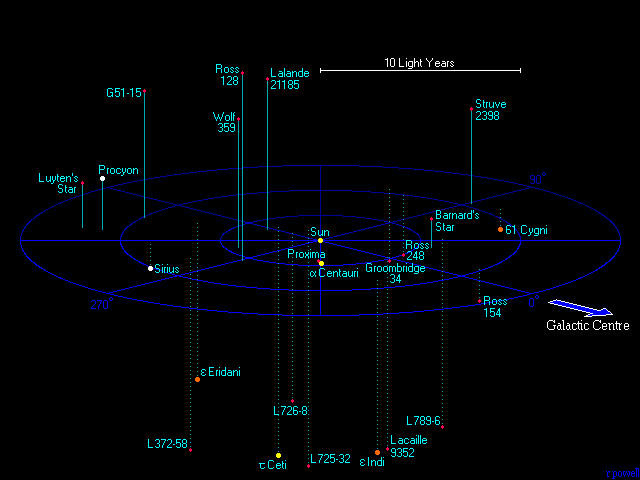
This map shows all the star systems that lie within 12.5 light years of our Sun. Most of the stars are red dwarfs - stars with a tenth of the Sun's mass and less than one hundredth the luminosity. Roughly eighty percent of all the stars in the universe are red dwarfs, and the nearest star - Proxima - is a typical example.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.